Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetases: Unraveling the Molecular Code of Life

Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) are a class of enzymes that play a fundamental role in protein synthesis, the process that converts genetic information into functional proteins. These enzymes catalyze the attachment of amino acids to their cognate transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in the growing polypeptide chain. Beyond their essential role in protein synthesis, aaRSs have emerged as important players in diverse biological processes, including gene expression, cell signaling, and immune function. This comprehensive article delves into the multifaceted world of aaRSs, exploring their intricate functions in biology and medicine.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| Hardcover | : | 324 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.19 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6 x 0.75 x 9 inches |
| File size | : | 6387 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 463 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Classification and Diversity
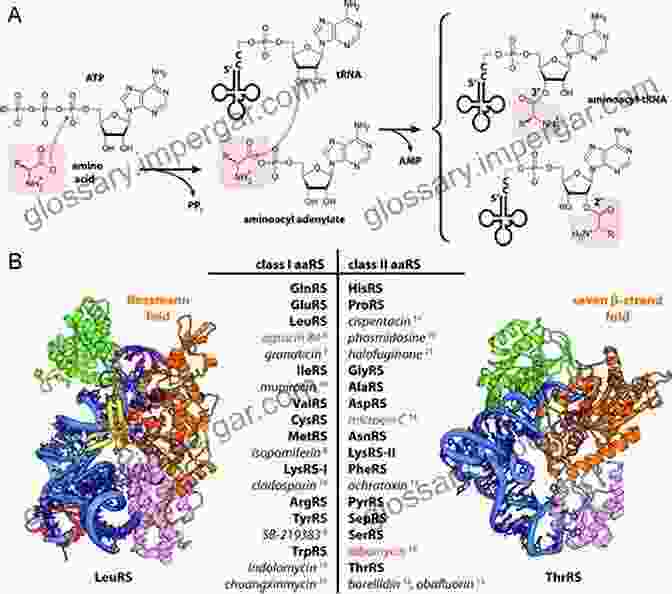
aaRSs are classified into two major classes based on their structural and catalytic mechanisms: Class I and Class II. Class I aaRSs utilize an ATP-dependent mechanism and consist of two catalytic domains, an aminoacylation domain and an editing domain. Class II aaRSs, on the other hand, employ an ATP-independent mechanism and have a single catalytic domain. There are 20 different aaRSs, each specific for a particular amino acid, ensuring the precise incorporation of amino acids into the growing polypeptide chain.
Mechanisms of Aminoacylation
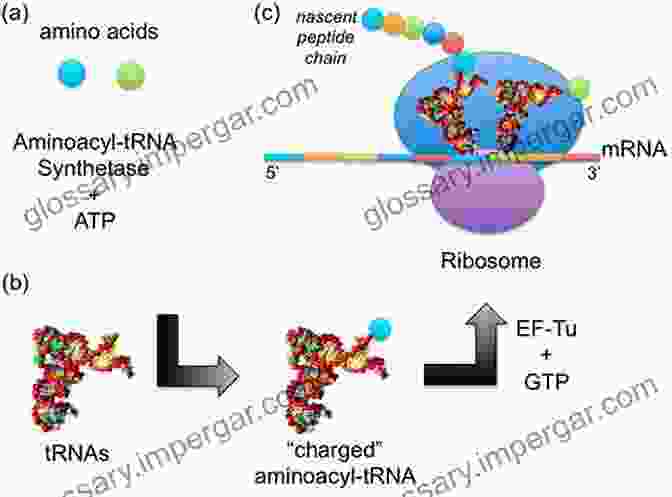
The central function of aaRSs is to attach amino acids to their cognate tRNA molecules. This process, known as aminoacylation, involves two distinct steps: amino acid activation and tRNA recognition. During amino acid activation, the aaRS binds to an amino acid and ATP, forming an aminoacyl-adenylate intermediate. In the subsequent step, the aaRS recognizes and binds to a specific tRNA molecule that is complementary to the amino acid. The aminoacyl-adenylate intermediate is then transferred to the 3'-end of the tRNA, forming an aminoacyl-tRNA conjugate.
Editing and Proofreading
The fidelity of protein synthesis relies heavily on the ability of aaRSs to discriminate between correct and incorrect amino acid-tRNA pairings. To ensure accuracy, aaRSs employ a two-step editing process. The first step involves kinetic discrimination, where the aaRS preferentially binds to the correct amino acid. If an incorrect amino acid is bound, the aaRS may hydrolyze the aminoacyl-adenylate intermediate, preventing its transfer to the tRNA. The second step involves post-transfer editing, where the aaRS checks the accuracy of the aminoacyl-tRNA conjugate. If an incorrect amino acid is incorporated, the aaRS may hydrolyze the aminoacyl-tRNA bond, releasing the amino acid and allowing for the correct amino acid to be incorporated.
Beyond Protein Synthesis
While their primary role lies in protein synthesis, aaRSs have been implicated in a wide range of cellular processes beyond translation. These include:
- Gene expression: aaRSs can regulate gene expression by controlling the availability of specific tRNA molecules. This regulation can influence the translation of specific proteins, thereby affecting cellular functions.
- Cell signaling: aaRSs can act as signaling molecules, transducing signals from the cytoplasm to the nucleus or vice versa. They can interact with other proteins and participate in signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
- Immune function: aaRSs have been linked to immune responses. They can activate immune cells, regulate cytokine production, and participate in antigen presentation. Dysregulation of aaRSs has been associated with autoimmune diseases and immune disFree Downloads.
Clinical Significance
Dysregulation of aaRSs has been implicated in various human diseases, including:
- Neurological disFree Downloads: Mutations in aaRS genes have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
- Cancer: Aberrant expression or activity of aaRSs has been observed in several types of cancer, suggesting their involvement in tumorigenesis and progression.
- Autoimmune diseases: Dysregulation of aaRSs has been associated with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Understanding the molecular mechanisms and clinical significance of aaRSs holds great potential for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for these diseases.
Therapeutic Potential
The emerging role of aaRSs in human diseases has sparked interest in their therapeutic potential. Several approaches are being explored, including:
- Inhibition of aaRSs: Small molecule inhibitors of aaRSs are being developed to target specific aaRSs involved in disease states. These inhibitors could be used to modulate aaRS activity and restore normal cellular function.
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy approaches aim to correct genetic defects in aaRS genes that are associated with diseases. This could involve introducing functional copies of the aaRS gene or using gene editing techniques to repair mutations.
- Immune modulation: Given the involvement of aaRSs in immune function, immunotherapeutic strategies that target aaRSs could be developed to treat autoimmune diseases or enhance antitumor immunity.
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases are essential enzymes that play a pivotal role in protein synthesis and other crucial cellular processes. Their diverse functions extend beyond translation, encompassing gene expression, cell signaling, and immune function. Dysregulation of aaRSs has been linked to various human diseases, highlighting their potential as therapeutic targets. Ongoing research continues to unravel the intricate mechanisms of aaRSs, opening up new avenues for the development of novel treatments for a range of diseases.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| Hardcover | : | 324 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.19 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6 x 0.75 x 9 inches |
| File size | : | 6387 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 463 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Gene Kopelson
Gene Kopelson Hakeem Seriki
Hakeem Seriki Sara Manasseh
Sara Manasseh Laurence Currie
Laurence Currie Robert O Friedel
Robert O Friedel Paul Stern
Paul Stern Gayle Pruitt
Gayle Pruitt Geoff Layton
Geoff Layton Gordon Graham
Gordon Graham Sarah K Fields
Sarah K Fields Giovanni Rigters
Giovanni Rigters Gordon Claridge
Gordon Claridge George D Snell
George D Snell Grace M Giesel
Grace M Giesel William Bleasdell Cameron
William Bleasdell Cameron Julie Catalano Msw Licsw
Julie Catalano Msw Licsw Ms Soup
Ms Soup Temitope James
Temitope James George Beebe
George Beebe Jan Silvious
Jan Silvious
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Paulo CoelhoExplore the Culinary Crossroads: Foreign Foods in Seventeenth Century England
Paulo CoelhoExplore the Culinary Crossroads: Foreign Foods in Seventeenth Century England Mario SimmonsFollow ·5.7k
Mario SimmonsFollow ·5.7k Corey GreenFollow ·3.8k
Corey GreenFollow ·3.8k David BaldacciFollow ·13k
David BaldacciFollow ·13k Doug PriceFollow ·10.1k
Doug PriceFollow ·10.1k Isaac MitchellFollow ·17.9k
Isaac MitchellFollow ·17.9k Josh CarterFollow ·5.9k
Josh CarterFollow ·5.9k Clark BellFollow ·10.8k
Clark BellFollow ·10.8k Evan HayesFollow ·8.6k
Evan HayesFollow ·8.6k

 Harry Cook
Harry CookUnraveling the Interplay: Tumor Biology, Inflammation,...
Cancer, a complex and multifaceted...

 H.G. Wells
H.G. WellsHistory and Archives Contribute to the Success of Space...
Space exploration is a complex and...

 Jaden Cox
Jaden CoxThe Essential Guide to Doctor Who! Dive into the 50...
Prepare yourself for a...

 Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor ColeridgeUnveiling the Secrets of the Laboratory: The Laboratory...
In the realm of biomedical research, the...

 Branden Simmons
Branden SimmonsLiquid Crystal Sensors: Unlocking the Future of Sensing...
In the ever-evolving...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| Hardcover | : | 324 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.19 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6 x 0.75 x 9 inches |
| File size | : | 6387 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 463 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |